
Model Building Report
This document lists the results for the homology modelling project "Proofreading exoribonuclease nsp14 (ExoN) | P0DTD1 PRO_0000449631" submitted to SWISS-MODEL workspace on May 5, 2023, 9:33 p.m..The submitted primary amino acid sequence is given in Table T1.
If you use any results in your research, please cite the relevant publications:
- Waterhouse A, Bertoni M, Bienert S, Studer G, Tauriello G, Gumienny R, Heer FT, de Beer TAP, Rempfer C, Bordoli L, Lepore R, Schwede TSWISS-MODEL: homology modelling of protein structures and complexes.Nucleic Acids Res 46, W296-W303. (2018)
 29788355
29788355 10.1093/nar/gky427
10.1093/nar/gky427 - Bienert S, Waterhouse A, de Beer TAP, Tauriello G, Studer G, Bordoli L, Schwede TThe SWISS-MODEL Repository - new features and functionality.Nucleic Acids Res 45, D313-D319. (2017)
 27899672
27899672 10.1093/nar/gkw1132
10.1093/nar/gkw1132 - Studer G, Tauriello G, Bienert S, Biasini M, Johner N, Schwede TProMod3 - A versatile homology modelling toolbox.PLOS Comp Biol 17(1), e1008667. (2021)
 33507980
33507980 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008667
10.1371/journal.pcbi.1008667 - Studer G, Rempfer C, Waterhouse AM, Gumienny R, Haas J, Schwede TQMEANDisCo - distance constraints applied on model quality estimation.Bioinformatics 36, 1765-1771. (2020)
 31697312
31697312 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz828
10.1093/bioinformatics/btz828 - Bertoni M, Kiefer F, Biasini M, Bordoli L, Schwede TModeling protein quaternary structure of homo- and hetero-oligomers beyond binary interactions by homology.Scientific Reports 7. (2017)
 28874689
28874689 10.1038/s41598-017-09654-8
10.1038/s41598-017-09654-8
Results
The SWISS-MODEL template library (SMTL version 2023-05-05, PDB release 2023-04-28) was searched with for evolutionary related structures matching the target sequence in Table T1. For details on the template search, see Materials and Methods. Overall 90 templates were found (Table T2).
Models
The following model was built (see Materials and Methods "Model Building"):
Model #02 |
File | Built with | Oligo-State | Ligands | GMQE | QMEANDisCo Global |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
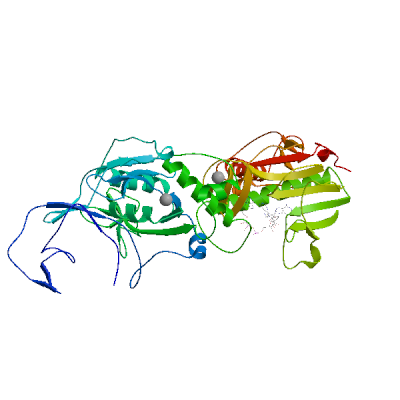
|
PDB | ProMod3 3.3.0 | monomer |
1 x G3A: GUANOSINE-P3-ADENOSINE-5',5'-TRIPHOSPHATE;
1 x MG: MAGNESIUM ION; 1 x SAH: S-ADENOSYL-L-HOMOCYSTEINE; 1 x ZN: ZINC ION; |
0.86 | 0.79 ± 0.05 |
|
|
| Template | Seq Identity | Oligo-state | QSQE | Found by | Method | Resolution | Seq Similarity | Range | Coverage | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5c8s.1.B | 95.07 | monomer | 0.00 | HHblits | X-ray | 3.33Å | 0.62 | 1 - 525 | 1.00 | Guanine-N7 methyltransferase |
Included Ligands
| Ligand | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 x G3A | GUANOSINE-P3-ADENOSINE-5',5'-TRIPHOSPHATE |
| 1 x MG | MAGNESIUM ION |
| 1 x SAH | S-ADENOSYL-L-HOMOCYSTEINE |
| 1 x ZN | ZINC ION |
Excluded ligands
| Ligand Name.Number | Reason for Exclusion | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ZN.1 | Binding site not conserved. | ZINC ION |
| ZN.2 | Binding site not conserved. | ZINC ION |
| ZN.3 | Clashing with protein. | ZINC ION |
| ZN.5 | Clashing with protein. | ZINC ION |
Target AENVTGLFKDCSKVITGLHPTQAPTHLSVDTKFKTEGLCVDIPGIPKDMTYRRLISMMGFKMNYQVNGYPNMFITREEAI
5c8s.1.B AENVTGLFKDCSKIITGLHPTQAPTHLSVDIKFKTEGLCVDIPGIPKDMTYRRLISMMGFKMNYQVNGYPNMFITREEAI
Target RHVRAWIGFDVEGCHATREAVGTNLPLQLGFSTGVNLVAVPTGYVDTPNNTDFSRVSAKPPPGDQFKHLIPLMYKGLPWN
5c8s.1.B RHVRAWIGFDVEGCHATRDAVGTNLPLQLGFSTGVNLVAVPTGYVDTENNTEFTRVNAKPPPGDQFKHLIPLMYKGLPWN
Target VVRIKIVQMLSDTLKNLSDRVVFVLWAHGFELTSMKYFVKIGPERTCCLCDRRATCFSTASDTYACWHHSIGFDYVYNPF
5c8s.1.B VVRIKIVQMLSDTLKGLSDRVVFVLWAHGFELTSMKYFVKIGPERTCCLCDKRATCFSTSSDTYACWNHSVGFDYVYNPF
Target MIDVQQWGFTGNLQSNHDLYCQVHGNAHVASCDAIMTRCLAVHECFVKRVDWTIEYPIIGDELKINAACRKVQHMVVKAA
5c8s.1.B MIDVQQWGFTGNLQSNHDQHCQVHGNAHVASCDAIMTRCLAVHECFVKRVDWSVEYPIIGDELRVNSACRKVQHMVVKSA
Target LLADKFPVLHDIGNPKAIKCVPQADVEWKFYDAQPCSDKAYKIEELFYSYATHSDKFTDGVCLFWNCNVDRYPANSIVCR
5c8s.1.B LLADKFPVLHDIGNPKAIKCVPQAEVEWKFYDAQPCSDKAYKIEELFYSYATHHDKFTDGVCLFWNCNVDRYPANAIVCR
Target FDTRVLSNLNLPGCDGGSLYVNKHAFHTPAFDKSAFVNLKQLPFFYYSDSPCESHGKQVVSDIDYVPLKSATCITRCNLG
5c8s.1.B FDTRVLSNLNLPGCDGGSLYVNKHAFHTPAFDKSAFTNLKQLPFFYYSDSPCESHGKQVVSDIDYVPLKSATCITRCNLG
Target GAVCRHHANEYRLYLDAYNMMISAGFSLWVYKQFDTYNLWNTFTRLQ
5c8s.1.B GAVCRHHANEYRQYLDAYNMMISAGFSLWIYKQFDTYNLWNTFTRLQ
Materials and Methods
Template Search
Template search with has been performed against the SWISS-MODEL template library (SMTL, last update: 2023-05-05, last included PDB release: 2023-04-28).
Model Building
Models are built based on the target-template alignment using ProMod3 (Studer et al.). Coordinates which are conserved between the target and the template are copied from the template to the model. Insertions and deletions are remodelled using a fragment library. Side chains are then rebuilt. Finally, the geometry of the resulting model is regularized by using a force field.
Model Quality Estimation
The global and per-residue model quality has been assessed using the QMEAN scoring function (Studer et al.).
Ligand Modelling
Ligands present in the template structure are transferred by homology to the model when the following criteria are met: (a) The ligands are annotated as biologically relevant in the template library, (b) the ligand is in contact with the model, (c) the ligand is not clashing with the protein, (d) the residues in contact with the ligand are conserved between the target and the template. If any of these four criteria is not satisfied, a certain ligand will not be included in the model. The model summary includes information on why and which ligand has not been included.
Oligomeric State Conservation
The quaternary structure annotation of the template is used to model the target sequence in its oligomeric form. The method (Bertoni et al.) is based on a supervised machine learning algorithm, Support Vector Machines (SVM), which combines interface conservation, structural clustering, and other template features to provide a quaternary structure quality estimate (QSQE). The QSQE score is a number between 0 and 1, reflecting the expected accuracy of the interchain contacts for a model built based a given alignment and template. Higher numbers indicate higher reliability. This complements the GMQE score which estimates the accuracy of the tertiary structure of the resulting model.
References
- Camacho C, Coulouris G, Avagyan V, Ma N, Papadopoulos J, Bealer K, Madden TLBLAST+: architecture and applications.BMC Bioinformatics, 10, 421-430. (2009)
 20003500
20003500 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421
10.1186/1471-2105-10-421 - Steinegger M, Meier M, Mirdita M, Vöhringer H, Haunsberger SJ, Söding JHH-suite3 for fast remote homology detection and deep protein annotation.BMC Bioinformatics 20, 473. (2019)
 31521110
31521110 10.1186/s12859-019-3019-7
10.1186/s12859-019-3019-7
Table T1:
Primary amino acid sequence for which templates were searched and models were built.
VGTNLPLQLGFSTGVNLVAVPTGYVDTPNNTDFSRVSAKPPPGDQFKHLIPLMYKGLPWNVVRIKIVQMLSDTLKNLSDRVVFVLWAHGFELTSMKYFVK
IGPERTCCLCDRRATCFSTASDTYACWHHSIGFDYVYNPFMIDVQQWGFTGNLQSNHDLYCQVHGNAHVASCDAIMTRCLAVHECFVKRVDWTIEYPIIG
DELKINAACRKVQHMVVKAALLADKFPVLHDIGNPKAIKCVPQADVEWKFYDAQPCSDKAYKIEELFYSYATHSDKFTDGVCLFWNCNVDRYPANSIVCR
FDTRVLSNLNLPGCDGGSLYVNKHAFHTPAFDKSAFVNLKQLPFFYYSDSPCESHGKQVVSDIDYVPLKSATCITRCNLGGAVCRHHANEYRLYLDAYNM
MISAGFSLWVYKQFDTYNLWNTFTRLQ
Table T2:
| Template | Seq Identity | Oligo-state | QSQE | Found by | Method | Resolution | Seq Similarity | Coverage | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7n0d.1.H | 99.81 | homo-tetramer | 0.51 | HHblits | EM | NA | 0.63 | 1.00 | Proofreading exoribonuclease |
| 7n0d.1.B | 99.81 | homo-tetramer | 0.51 | HHblits | EM | NA | 0.63 | 1.00 | Proofreading exoribonuclease |
| 7n0d.1.D | 99.81 | homo-tetramer | 0.51 | HHblits | EM | NA | 0.63 | 1.00 | Proofreading exoribonuclease |
| 5nfy.4.A | 94.88 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 3.38Å | 0.62 | 1.00 | Polyprotein 1ab |
| 5nfy.2.A | 94.88 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 3.38Å | 0.62 | 1.00 | Polyprotein 1ab |
| 5nfy.1.A | 94.88 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 3.38Å | 0.62 | 1.00 | Polyprotein 1ab |
| 5nfy.3.A | 94.88 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 3.38Å | 0.62 | 1.00 | Polyprotein 1ab |
| 7n0c.1.B | 99.81 | monomer | - | HHblits | EM | NA | 0.63 | 1.00 | Proofreading exoribonuclease |
| 5c8s.1.B | 95.07 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 3.33Å | 0.62 | 1.00 | Guanine-N7 methyltransferase |
| 5c8t.1.B | 95.07 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 3.20Å | 0.62 | 1.00 | Guanine-N7 methyltransferase |
| 7n0b.1.B | 100.00 | monomer | - | HHblits | EM | NA | 0.63 | 1.00 | Proofreading exoribonuclease |
| 7egq.1.H | 100.00 | monomer | - | HHblits | EM | NA | 0.63 | 1.00 | Proofreading exoribonuclease |
| 7egq.1.P | 100.00 | monomer | - | HHblits | EM | NA | 0.63 | 1.00 | Proofreading exoribonuclease |
| 7eiz.1.I | 100.00 | monomer | - | HHblits | EM | NA | 0.63 | 1.00 | Proofreading exoribonuclease |
| 7tw7.1.A | 90.20 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 1.62Å | 0.59 | 0.48 | Transcription factor ETV6,Proofreading exoribonuclease nsp14 chimera |
| 7tw8.1.A | 90.20 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 1.55Å | 0.59 | 0.48 | Transcription factor ETV6,Proofreading exoribonuclease nsp14 chimera |
| 7tw9.1.A | 90.20 | monomer | - | HHblits | X-ray | 1.41Å | 0.59 | 0.48 | Transcription factor ETV6,Proofreading exoribonuclease nsp14 chimera |
The table above shows the top 17 filtered templates. A further 72 templates were found which were considered to be less suitable for modelling than the filtered list.
5c8s.2.B, 5c8t.2.B, 5c8u.2.B, 5skw.1.A, 5skx.1.A, 5sky.1.A, 5skz.1.A, 5sl0.1.A, 5sl1.1.A, 5sl2.1.A, 5sl3.1.A, 5sl4.1.A, 5sl5.1.A, 5sl6.1.A, 5sl7.1.A, 5sl8.1.A, 5sl9.1.A, 5sla.1.A, 5slb.1.A, 5slc.1.A, 5sld.1.A, 5sle.1.A, 5slf.1.A, 5slg.1.A, 5slh.1.A, 5sli.1.A, 5slj.1.A, 5slk.1.A, 5sll.1.A, 5slm.1.A, 5sln.1.A, 5slo.1.A, 5slp.1.A, 5slq.1.A, 5slr.1.A, 5sls.1.A, 5slt.1.A, 5slu.1.A, 5slv.1.A, 5slw.1.A, 5slx.1.A, 5sly.1.A, 5slz.1.A, 5sm0.1.A, 5sm1.1.A, 5sm2.1.A, 5sm3.1.A, 5sm4.1.A, 5sm5.1.A, 5sm6.1.A, 5sm7.1.A, 5sm8.1.A, 5sm9.1.A, 5sma.1.A, 5smb.1.A, 5smc.1.A, 5smd.1.A, 5sme.1.A, 5smf.1.A, 5smg.1.A, 5smh.1.A, 5smi.1.A, 5smk.1.A, 7diy.1.B, 7mc5.1.A, 7mc6.1.A, 7n0d.1.J, 7qgi.1.A, 7qif.1.A, 7r2v.1.A, 7r2v.2.A, 7tw7.1.A